
Ralph Shohet, M.D.
Director & Professor of Medicine
Center for Cardiovascular Research
John A. Burns School of Medicine
651 Ilalo Street, BSB 311
Honolulu, HI 96813
Email: shohet@hawaii.edu
Phone: (808) 692-1469
1. Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1
We are especially interested in myocardial ischemia and resulting hypoxia, the most common cause of death in the developed world. Hypoxia inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) is a transcription factor that is rapidly degraded under normal levels of cellular oxygen. When oxygen levels decrease, the protein accumulates and directs a cascade of gene regulation that determines the response to hypoxia. In our studies we have used a modified HIF-1α cDNA in which the degradation mechanisms no longer operate, resulting in constitutive activation of the protein. We have studied this mutated form in a tet-regulated transgenic line that expressed active HIF-1 in a normoxic environment in the hearts of adult mice. We have discovered effects of HIF in the heart that include, besides the expected transcriptional changes, modulation of micro-RNAs, mRNA splicing, and chromatin accessibility, all of which work in concert to direct the cardiac response to the stress of hypoxia.
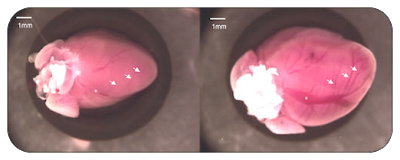
2. Ultrasound Target Microbubble Destruction (UTMD)
Though protein and gene therapy strategies are rapidly advancing, we have yet to develop an efficient, reliable method for local in vivo delivery. In the Shohet lab we work on a technique, termed ultrasound targeted microbubble destruction (UTMD), that directs local delivery of expression constructs to specific regions in a minimally invasive manner. Microbubbles, which are composed of a perfluorocarbon gas encapsulated in a polymer, protein, or lipid shell, are frequently, and safely, used as contrast agents for ultrasonic imaging of the cardiovascular system. An ultrasonic signal of the appropriate frequency can disrupt the bubbles. We have attached both plasmids and proteins to microbubbles, injected them into animals, and obtained efficient delivery to target organs by destroying the microbubbles with a properly guided ultrasonic signal. This is a platform technology with broad applicability. Presently we are using it to investigate delivery of gene therapy vectors to the liver in order to treat hemophilia, to the heart to investigate angiogenesis, to the kidney to treat anemia, and to the spleen to explore how this might modify the immune response to vaccines. We have been incorporating high intensity focused ultrasound into our studies, which produces exquisitely precise foci of transgene expression in target organs.
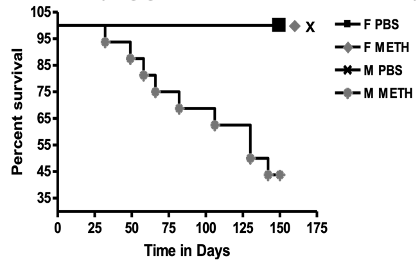
3. Methamphetamine Cardiomyopathy
Methamphetamine (meth) is a progressively more common and very toxic drug of abuse. We have developed a mouse model of meth cardiomyopathy, which is the most common cause of death from meth after overdose. Remarkably, we find that male mice are much more susceptible to meth cardiotoxicity than are female mice. This also appears to be the case in human patients as well. We are now exploring whether this is a function of the sex hormones or underlying genomic differences in the programming of chromatin.
Lee KCY, Williams AL, Andrukhiv A, Gerschenson M, Shohet RV. PKM2 regulates metabolic flux and oxidative stress in the murine heart. Physiol Reports, in press, 2024.
Anderson CA, Arthur JA, Zhang Y, Bharucha N, Karakikes I, and Shohet RV. Non-viral in vivo cytidine base editing in hepatocytes using focused ultrasound targeted microbubbles. Molecular Therapy-Nucleic Acids. 33:733-737, 2023. PMC10468349
Anderson CD, Walton CB, Shohet RV. A comparison of focused and unfocused ultrasound for microbubble-mediated gene delivery. Ultrasound in Med and Biol. 2021.
Williams AL, Khadka VS, Anagaran MCT, Lee K, Avelar A, Deng Y and Shohet RV. MiR-125 family regulates XIRP1 and FIH in response to myocardial infarction. Phys Gen. 52:358-368, 2020. PMC7473889
Williams AL, Walton CB, MacCannell D, Avelar A, Shohet RV. HIF1 regulation of miR-29c impairs SERCA2 expression and cardiac contractility. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 316:H554-655, 2019. PMC6459310
Marcinko MC, Darrow AL, Tuia AJ, Shohet RV. Sex influences susceptibility to methamphetamine cardiomyopathy in mice. Physiol Reports, 7(5), e14036, 2019. PMC6424857.
Schunke KJ, Walton CB, Veal DR, Mafnas CT, Anderson CD, Williams AL, Shohet RV. Protein Kinase C Binding Protein 1(PRKCBP1) Inhibits Hypoxia Inducible Factor 1 (HIF-1) in the Heart. Cardiovasc Res. 115:1332-1342, 2019. PMC6587917
Anderson CD, Moisyadi S, Avelar A, Walton CB*, and Shohet RV*. Ultrasound targeted hepatic delivery of Factor IX in hemophiliac mice. Gene Therapy. 23:510-519, 2016 (*shared first authors).
Bekeredjian R*, Walton CB*, MacCannell KA, Kruse F, Outten JT, Sutcliffe D, Gerard RD, Bruick RK, Shohet RV. Conditional HIF-1α expression produces a reversible cardiomyopathy. PLoS One. 5:e11693, 2010 (*shared first authors).
Zhao XS, Pan W, Bekeredjian R, Shohet RV. Endogenous Endothelin-1 Is Required for Cardiomyocyte Survival In Vivo. Circulation.114(8):830-837, 2006.
Shohet RV, Chen S, Zhou Y-T, Wang Z, Meidell RS, Unger R, Grayburn PA, Ultrasonic disruption of albumin microbubbles directs gene delivery to the myocardium. Circulation. 101:2554-2556, 2000.